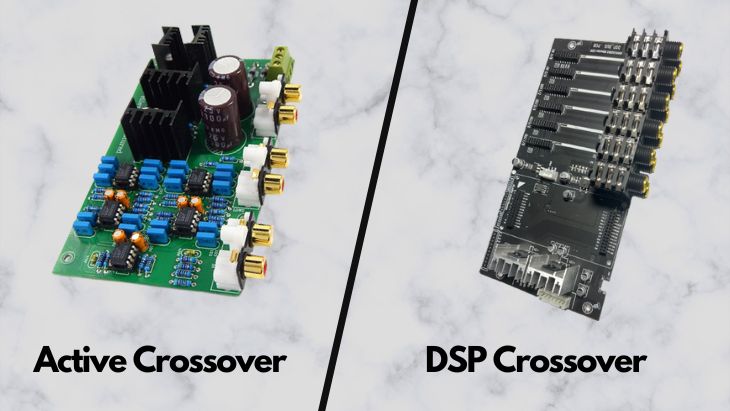
There are many components that make up an audio system. Speakers are arguably the most important component of any audio system. Although other components matter, it is the speakers that turn all the current and voltage into audible sound. Crossovers are extremely important in the proper functioning of a speaker. Also, DSPs come in handy in digital audio processing. In this article, we will discuss active crossover vs DSP in detail.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Variable | Active Crossover | DSP |
| Size | Larger | Very small |
| Portability | Less portable | More portable |
| Mode of operation | Splitting signals | Mathematical operations |
| Complexity | Simple | Very complex |
| Application | Loudspeakers | Loudspeakers, headphones, smart speakers, smartphones |
| Cost | Affordable | Pricey |
What is an Active Crossover?
Crossovers are available as passive crossovers and active crossovers. For the purpose of this article, we will take you through active crossovers. Basically, an active crossover refers to a device that modifies audio signals before amplification. An active crossover only works on preamp signals or line-level signals. It combines resistors, capacitors, and operational amps to split an entire audio frequency into different frequency ranges.
Unlike passive crossovers, active crossovers can increase the level of an input signal as long as the filters are powered. Also, some active crossovers come with extra functions such as bass boost circuits and remote level control.
In active crossovers, a power amp is connected directly to the speaker. The signal that feeds the power amp comes from the active crossover. The signal that the active crossover filters comes from an audio source such as a head unit or preamp. The crossover filters the signal into various bands and sends them to the amp for amplification.
Advantages of an Active Crossover
When comparing active crossover vs DSP, it will help to discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each. To start with, the advantages of an active crossover include:
- Most active crossovers are adjustable. You can move a switch or knob to alter the crossover frequency. Thus, they are ideal for use with most speaker systems.
- Most active crossovers feature level controls for easier fine-tuning of the output level of the tweeter and midrange drivers depending on the mounting locations.
- They do not rely on an amplifier before filtering the signal.
- They are not highly sensitive to temperature changes, making them highly accurate.
- If one amp channel is hooked to the crossover clips, the distortion does not affect other channels.
Shortcomings of Active Crossovers
- Most active crossovers come with fixed attenuation slopes such that you cannot alter them to compensate for any placement variations.
- Often challenging to determine the frequency you should cross speakers.
- If you set the frequency too low, you risk damaging the tweeters. If you set it too high, you risk getting distortion from midrange speakers.
- A dedicated amp channel is required for each speaker. The extra channels increase the overall cost of designing the audio system.
What is DSP?
DSP is an acronym for a digital signal processor. In audio applications, a DSP takes digital real-world audio signals and manipulates them mathematically. The mathematical functions done on the signal include dividing, multiplying, subtracting, and adding. The manipulation is done extremely fast.
Essentially, digital audio signals require processing to ensure the information they contain is converted or analyzed to another form of signal as needed. Processing is done either in an analog or digital format. For analog format, the data is converted using a digital to analog converter.
DSPs come in the form of chips. The chips are available in a wide range of performance points and sizes. Some are as small as those used in smart speakers for voice recognition while others are as large as those used in professional studio sound equipment or multi-channel DSPs in cars. Their main role is to speed up the process of executing audio-based algorithms and keep power consumption low.
Most devices that process audio are likely to have a DSP. For instance, smartphones come with a built-in DSP that decodes MP3 audio files, noise cancellation, voice recognition, and boosts bass. Also, wireless headphones come with DSP units that convert Bluetooth data into audio signals. Some home theatre speakers also come with DSP to decode data for surround sound experience.
Advantages of DSPs
Digital signal processors offer numerous advantages including:
- Minimal noise.
- Easy to encrypt digital signals.
- Possible to detect and correct errors.
- Easy to store data.
- Possible to transmit a lot of data
- Easy to modify data.
- DSPs work through wider frequencies.
- Possible to cascade DSP systems without any loading problems
- It is easy to implement complicated signal algorithms.
- You can easily upgrade DSP systems since they’re controlled by software.
- DSPs are more compact and lightweight.
Shortcomings of DSPs
- Most DSPs are expensive.
- High bandwidth is needed to transmit data.
- Additional components lead to more complexity.
- Requires specialized skills to program a DSP device.
Active Crossover Vs DSP – Final Thoughts
Active crossovers are a great pick, especially when you want to ensure the audio signal remains pure. Also, they do not require an amp before processing signals. However, you cannot upgrade an active crossover. You can only buy a new one if you need extra features that the current one does not offer.
On the other hand, DSPs are more portable and can be upgraded by updating the software that controls them. They are superb for use with compact audio devices such as smart speakers and headphones. Also, they consume very little power, making them ideal for portable speakers. However, DSPs are more expensive than active crossovers.
Michael Evanchuk is a San Francisco-based sound engineer with 20 years’ experience installing, troubleshooting, and repairing commercial, automotive, and household sound equipment. Evanchuk owns an auto stereo center, where he offers highly competitive car audio installation and repair services. He has written dozens of articles on different sound engineering topics, all of which have been published in leading journals, blogs, and websites.